Lean warehousing, and lean warehouse management, is a concept that has gained significant traction in the logistics and supply chain industry. It revolves around the idea of eliminating waste—be it in the form of time, effort, or resources—in warehouse operations to enhance efficiency and productivity. However, there are misconceptions about lean warehousing. Some view it as a mere cost-cutting measure, while others see it as a complex process that’s difficult to implement. In reality, lean warehousing is about creating value by streamlining processes, improving flow, and reducing non-value-adding activities.
Principles of Lean Warehousing
The principles of lean warehousing are rooted in the concepts of Muda (waste), Muri (overburden), and Mura (unevenness). Muda refers to activities that do not add value to the customer or the business. Muri represents overburdening resources or employees, and Mura signifies the unevenness or inconsistencies in business operations. By identifying and addressing these three aspects, warehouses can significantly improve their operations and efficiency.
Challenges in Implementing Lean Warehousing
Implementing lean practices in a warehouse is not without its challenges. These can range from resistance to change among staff, to the need for significant upfront investment in training and technology. Other challenges include the complexity of managing inventory in a lean environment and the need for a cultural shift towards continuous improvement. However, with the right approach and commitment, these challenges can be overcome.
Implementing Lean Practices in Warehouse Management
Implementing lean practices in warehouse management involves a systematic approach to identifying waste, implementing changes, and continuously improving processes. This can include changes to the physical layout of the warehouse to improve flow, implementing new technology to automate processes and reduce errors, and training staff in lean principles and techniques. It’s important to remember that implementing lean is not a one-time project, but a continuous process of improvement.
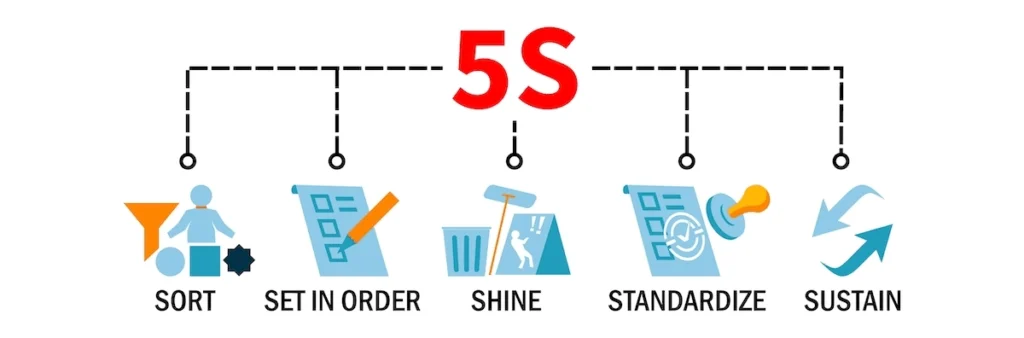
The 5S Model in Lean Warehousing
The 5S model, or 5S system, is a fundamental tool in lean warehousing. The five S’s stand for Sort (removing unnecessary items), Set in order (organizing items), Shine (cleaning the workspace), Standardize (creating consistent ways of performing tasks), and Sustain (maintaining and improving standards). Implementing 5S can help to create a more efficient and productive warehouse environment.
The Role of Kanban and Kaizen in Lean Warehousing
Kanban and Kaizen are two key methodologies in lean warehousing. Kanban is a visual system for managing work as it moves through a process, helping to manage workflow and reduce waste. Kaizen, on the other hand, is a strategy for continuous improvement, involving everyone in the organization from top management to warehouse floor workers. Both methodologies are key to creating a culture of continuous improvement in a lean warehouse.
Lean Warehousing and Technology
Technology plays a crucial role in supporting lean principles in a warehouse. Warehouse management systems (WMS), automated guided vehicles (AGVs), and robotics can all contribute to reducing waste and improving efficiency. For example, a WMS can optimize inventory tracking and order picking, while AGVs and robotics can automate repetitive tasks, reducing errors and freeing up staff for more complex tasks.
Lean Warehousing and Employee Training
Employee training is a key component of lean warehousing. Staff need to be trained in lean principles and techniques, and need to understand the reasons for implementing lean. Training can be provided through formal courses, on-the-job training, or continuous improvement teams. A well-trained workforce is more likely to be engaged and committed to the lean journey.
Lean Warehousing in Different Industries
While lean warehousing originated in the manufacturing sector, its principles can be applied in a variety of industries. In the retail industry, for example, lean can help to manage inventory and improve order fulfillment. In the food and beverage industry, lean can help to manage perishable items and reduce waste. Regardless of the industry, the principles of lean warehousing can help to improve efficiency and productivity.

Lean Warehousing and Sustainability
Lean warehousing can also contribute to sustainability goals. By reducing waste, improving energy efficiency, and promoting better resource utilization, lean warehousing can help to reduce a warehouse’s environmental footprint. This not only benefits the environment but can also lead to cost savings and an improved reputation for the business.
Benefits of Lean Warehousing
The benefits of lean warehousing are numerous. By reducing waste and improving efficiency, lean can lead to significant cost savings. It can also improve service levels, through more accurate order picking and faster order fulfillment. Furthermore, by creating a more organized and efficient work environment, lean warehousing can lead to improved employee morale and reduced turnover.
Conclusion
Lean warehousing is more than just a buzzword—it’s a proven methodology that can bring significant benefits to any warehouse operation. By focusing on eliminating waste, improving efficiency, and continuously improving, warehouses can become more productive, more efficient, and more sustainable. While implementing lean warehousing can be a challenge, the benefits it brings make it well worth the effort.
If you’re interested in implementing lean warehousing practices in your operation, Logimax is here to help. Our warehouse management system is designed with lean principles in mind, helping you to reduce waste, improve efficiency, and drive continuous improvement. Contact us today to learn more about how we can help you on your lean journey.



